| [1]Rieske P, Krynska B, Azizi SA. Human fibroblast-derived cell lines have characteristics of embryonic stem cells and cells of neuro-ectodermal origin.Differentiation. 2005;73(9-10): 474-483.
[2]Takahashi K, Yamanaka S.Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors.Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.
[3]Fox JL.FDA scrutinizes human stem cell therapies.Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(6):598-599.
[4]Thomson JA, Marshall VS. Primate embryonic stem cells. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1998;38:133-165.
[5]Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS,et al.Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts.Science. 1998;282(5391):1145-1147.
[6]Catalina P, Montes R, Ligero G,et al.Human ESCs predisposition to karyotypic instability: Is a matter of culture adaptation or differential vulnerability among hESC lines due to inherent properties. Mol Cancer. 2008;7:76.
[7]Dahl JA, Duggal S, Coulston N,et al.Genetic and epigenetic instability of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells expanded in autologous serum or fetal bovine serum.Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(8):1033-1042.
[8]De Temmerman N, Seneca S, Van Steirteghem A,et al.CTG repeat instability in a human embryonic stem cell line carrying the myotonic dystrophy type 1 mutation.Mol Hum Reprod. 2008;14(7):405-412.
[9]Gore A, Li Z, Fung HL,et al.Somatic coding mutations in human induced pluripotent stem cells.Nature. 2011;471 (7336): 63-67.
[10]Imreh MP, Gertow K, Cedervall J,et al. In vitro culture conditions favoring selection of chromosomal abnormalities in human ES cells.J Cell Biochem. 2006;99(2):508-516.
[11]Inzunza J, Sahlén S, Holmberg K,et al.Comparative genomic hybridization and karyotyping of human embryonic stem cells reveals the occurrence of an isodicentric X chromosome after long-term cultivation.Mol Hum Reprod. 2004;10(6):461-466.
[12]Liang Q, Conte N, Skarnes WC,et al.Extensive genomic copy number variation in embryonic stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(45):17453-17456.
[13]Närvä E, Autio R, Rahkonen N,et al.High-resolution DNA analysis of human embryonic stem cell lines reveals culture-induced copy number changes and loss of heterozygosity.Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(4):371-377.
[14]Taapken SM, Nisler BS, Newton MA,et al. Karotypic abnormalities in human induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells.Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(4):313-314.
[15]Martins-Taylor K, Nisler BS, Taapken SM,et al.Recurrent copy number variations in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(6):488-491.
[16]Martins-Taylor K, Xu RH.Concise review: Genomic stability of human induced pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cells. 2012;30(1): 22-27.
[17]Laurent LC, Ulitsky I, Slavin I,et al. Dynamic changes in the copy number of pluripotency and cell proliferation genes in human ESCs and iPSCs during reprogramming and time in culture.Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(1):106-118.
[18]Hussein SM, Batada NN, Vuoristo S,et al.Copy number variation and selection during reprogramming to pluripotency. Nature. 2011;471(7336):58-62.
[19]Mayshar Y, Ben-David U, Lavon N,et al. Identification and classification of chromosomal aberrations in human induced pluripotent stem cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(4):521-531.
[20]Lefort N, Feyeux M, Bas C,et al.Human embryonic stem cells reveal recurrent genomic instability at 20q11.21.Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(12):1364-1366.
[21]Närvä E, Autio R, Rahkonen N,et al.High-resolution DNA analysis of human embryonic stem cell lines reveals culture-induced copy number changes and loss of heterozygosity.Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(4):371-377.
[22]Spits C, Mateizel I, Geens M,et al.Recurrent chromosomal abnormalities in human embryonic stem cells.Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(12):1361-1363.
[23]Kim D, Kim CH, Moon JI,et al.Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells by direct delivery of reprogramming proteins.Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(6):472-476.
[24]Reuter VE.Origins and molecular biology of testicular germ cell tumors.Mod Pathol. 2005;18 Suppl 2:S51-60.
[25]Hanna J, Saha K, Pando B,et al.Direct cell reprogramming is a stochastic process amenable to acceleration.Nature. 2009; 462(7273):595-601.
[26]Laurent LC, Ulitsky I, Slavin I,et al. Dynamic changes in the copy number of pluripotency and cell proliferation genes in human ESCs and iPSCs during reprogramming and time in culture.Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(1):106-118.
[27]Vissers LE, Stankiewicz P. Microdeletion and microduplication syndromes.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;838:29-75.
[28]Mefford HC, Yendle SC, Hsu C,et al.Rare copy number variants are an important cause of epileptic encephalopathies. Ann Neurol. 2011;70(6):974-985.
[29]Abyzov A, Mariani J, Palejev D,et al.Somatic copy number mosaicism in human skin revealed by induced pluripotent stem cells.Nature. 2012;492(7429):438-442.
[30]Liu W, Li M, Qu J,et al.Reevaluation of the safety of induced pluripotent stem cells: a call from somatic mosaicism.Protein Cell. 2013;4(2):83-85.
[31]Dalgaard MD, Weinhold N, Edsgärd D,et al.A genome-wide association study of men with symptoms of testicular dysgenesis syndrome and its network biology interpretation.J Med Genet. 2012;49(1):58-65.
[32]Nakayama M.Cell Therapy Using Induced Pluripotent Stem (iPS) Cells Meets Next-Next Generation DNA Sequencing Technology.Curr Genomics. 2009;10(5):303-305. |
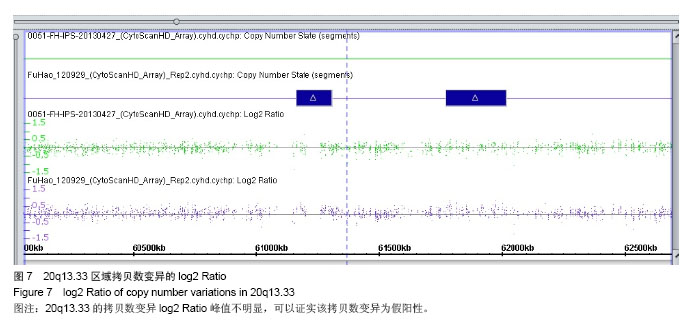
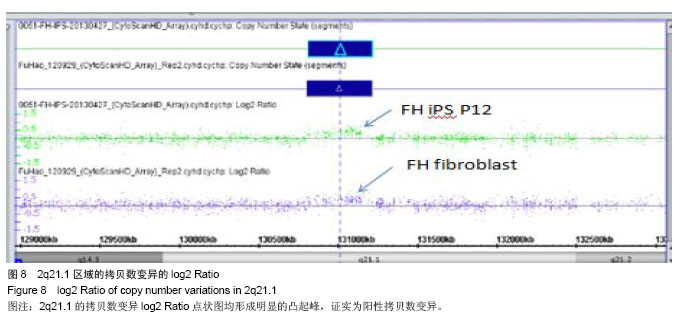

.jpg)